
healthcare workers who could accidentally prick themselves with an infected needle – but this risk is extremely low.people who have received a blood transfusion, transplant or other risk-prone procedures in countries that do not have strong screening for HIV.people who have had multiple sexual partners.people with a history of sexually transmitted infections, hepatitis B or hepatitis C.people who share sex toys with someone infected with HIV.people who have unprotected sex with somebody who has injected drugs and shared equipment.people who inject drugs and share equipment.women who have unprotected sex with men who have sex with men.people who engage in chemsex (using drugs to help or enhance sex).
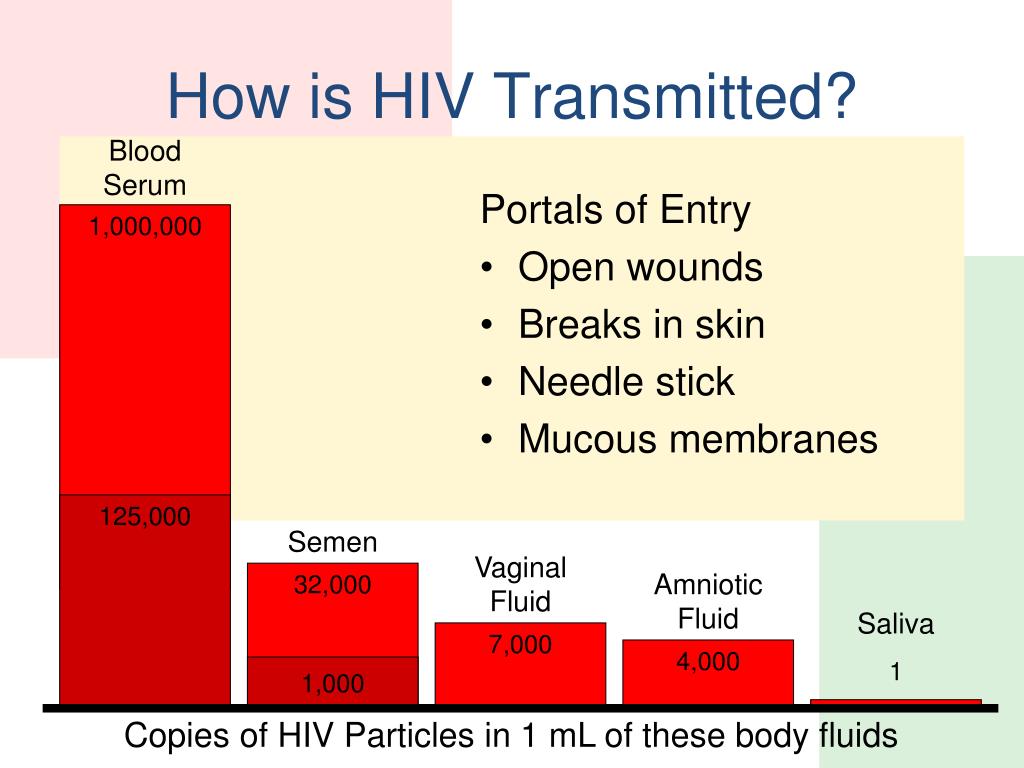
people who are from an area with high HIV rates.people with a current or previous partner who is from an area with high HIV rates.people with a current or previous partner with HIV.People who are at higher risk of becoming infected with HIV include: the person receiving oral sex has recently been infected with HIV and has a lot of the virus in their body, or another sexually transmitted infection.the person giving oral sex has mouth ulcers, sores or bleeding gums.It may also be possible to catch HIV through unprotected oral sex, but the risk is much lower. Most people diagnosed with HIV in the UK acquire the virus through unprotected vaginal or anal sex. HIV treatment significantly reduces the risk of someone with HIV passing it on. People with HIV can pass the virus on more easily in the weeks following infection. In the UK, most cases of HIV are caused by having sex with a person who has HIV without using a condom.Ī person with HIV can pass the virus on to others even if they do not have any symptoms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
